Exploring Gleam, a type-safe language on the BEAM!
Published on Saturday, June 1st, 2024
From Erlang, to Elixir and now, GLEAM!?
If you know me, you’d probably say, “Omg Chris, yet another new language???!!!“. The truth is, this is the only way I found to keep my motivation as a software engineer. A new language means a new way of both building and thinking. I’m trying to stay open-minded when it comes to my craft. I’ll just get the best out of this new experience and move on. In this article, I’m going to talk about Gleam, how I found it, and why I’m already LOVING it.

How I heard about Gleam?
Gleam V1 launched on March 4th 2024. As a built different engineer, I found out about it back in November 2023, when I started being seriously interested in Elixir.
The thing that always kind of put me off regarding Elixir was the dynamic typing. I’m a static typing person; it solves a LOT of common issues in my day-to-day job and provides cool benefits like:
- Less runtime errors, since the compiler YELLS at you when something is wrong about your code structure.
- Trust in what goes to production, since it was approved by the boss (the compiler).
- Code with typing indications is often (not always, but still, often) clearer and easier to understand. If the documentation is incomplete or non-existent, you still have something to go by, and new engineers can start contributing faster.
- Coding by thinking about the data structure FIRST, and then, the implementation matches my thinking process.
Anyway, you get it, I a type-sexual.
So, one day, I was googling “Static typing elixir”, and I saw Gleam in the results. What did I do? I just ignored the thing and moved on.
WHY ?
Because I’m more mature than ever. Like look, I did my due diligence on Gleam: adoption, use cases, versions (it was on v0.something), and I wasn’t impressed. I thought that Gleam was super early, a cool gimmick, an experimental toy, but it stayed somewhere in my brain, in the box where I put the stuff I might get into, but not RIGHT NOW.
What Gleam brings to the table
Fast forward, it’s March 1st, 2024: Gleam is officially on V1. I read the changelog, I get the SDK to play with the language and folks… the vibes are IMMACULATE. I’m starting to regret the time I had the occasion to be involved super early (I know it’s dumb), but as they (idk who’s “they”) said, better late than never.
I’ll go through the features I love the most and tell you what I like, and what can be better.
Types and structures
I think it’s BEAUTIFUL, like:
type Vehicle {
Car(make: String, brand: String)
Skateboard(brand: String)
Spaceship(year: Int)
}
What you’re seeing here is a Gleam custom type or Record, with Vehicle
being the type’s name, Car, Skateboard, and Spaceship being the
constructors available for this type. This is basically a tagged union, or if
you prefer, some sort of enumeration, where each member gets its own set of
attributes. It’s being used like:
let my_car = Car("Honda", "Civic")
and it allows pretty cool structures, like this cute pattern matching:
fn get_driving_requirements(vehicule: Vehicle) -> String {
case vehicule {
Car(make, brand) ->
"To drive the car "
<> make
<> " "
<> brand
<> ", your need a driver licence."
Skateboard(brand) -> "Anybody can ride a " <> brand <> " skateboard!"
Spaceship(_) -> "You need to be a NASA astronaut for that!"
}
}
Let’s spend some time on the function above:
get_driving_requirementstakes only oneVehicletype argument and returns aString. Both Gleam’s compiler and LSP will let you know if any of those conditions are not respected. Specifying what a function returns in Gleam is optional; due to type inference, Gleam will understand it anyway.- In the function’s body, you can see the
casestructure. This is how you perform pattern matching, which is essentially a switch control on steroids. Using acase, you can execute code path if a specific pattern is matched for a given variable. It’s pretty crazy how deeply you leverage this technique. In my example, I check every possible constructor for thevehiclevariable. Once again, the tooling will alert you if your pattern matching is not exhaustive (safety first!).
It’s super expressive, the code is concise and elegant (to me).
Gleam’s tooling…
…is CRAZY. Like, crazy CRAZY. I spent so much time in the cursed lands of
Javascript that I forgot grass could be THIS green elsewhere. The only thing you
need to do it to install the gleam CLI. To do so, I used
asdf, but you can do the same using any other package
manager like Homebrew. What does the gleam command do? Check this out:
❯ gleam
gleam 1.2.0-rc1
Usage: gleam <COMMAND>
Commands:
add Add new project dependencies
build Build the project
check Type check the project
clean Clean build artifacts
deps Work with dependency packages
docs Render HTML documentation
export Export something useful from the Gleam project
fix Rewrite deprecated Gleam code
format Format source code
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
hex Work with the Hex package manager
lsp Run the language server, to be used by editors
new Create a new project
publish Publish the project to the Hex package manager
remove Remove project dependencies
run Run the project
shell Start an Erlang shell
test Run the project tests
update Update dependency packages to their latest versions
Options:
-h, --help Print help
-V, --version Print version
- package manager ➡️
gleam add - repl ➡️
gleam shell - test runner ➡️
gleam test - formatter ➡️
gleam format - lsp ➡️
gleam lsp - and more…
All you need to get started with Gleam is already in this CLI. You dont’t have ANYTHING else check, there’s ZERO decision paralysis: THIS-IS-WHAT-WE-WANT. Javascript makes you pick a tool among hundred of options, for each tool provided in Gleam’s CLI.
One more thing: each language version comes bundled with its own set of tools; to prevent tooling incompabilities.
Let’s reuse the previous example:
import gleam/io
/// This is some type related to type Vehicle
type Vehicle {
/// Car type used for... a car I guess...
Car(make: String, brand: String)
Skateboard(brand: String)
Spaceship(year: Int)
}
fn get_driving_requirements(vehicle: Vehicle) -> String {
case vehicle {
Car(make, brand) ->
"To drive the car "
<> make
<> " "
<> brand
<> ", your need a driver licence."
Spaceship(_) -> "You need to be a NASA astronaut for that!"
Skateboard(brand) -> "Anybody can ride a " <> brand <> " skateboard!"
}
}
pub fn main() {
get_driving_requirements(Car(make: "Hyundai", brand: "Kona"))
io.println("Hello from gl_playground!")
}
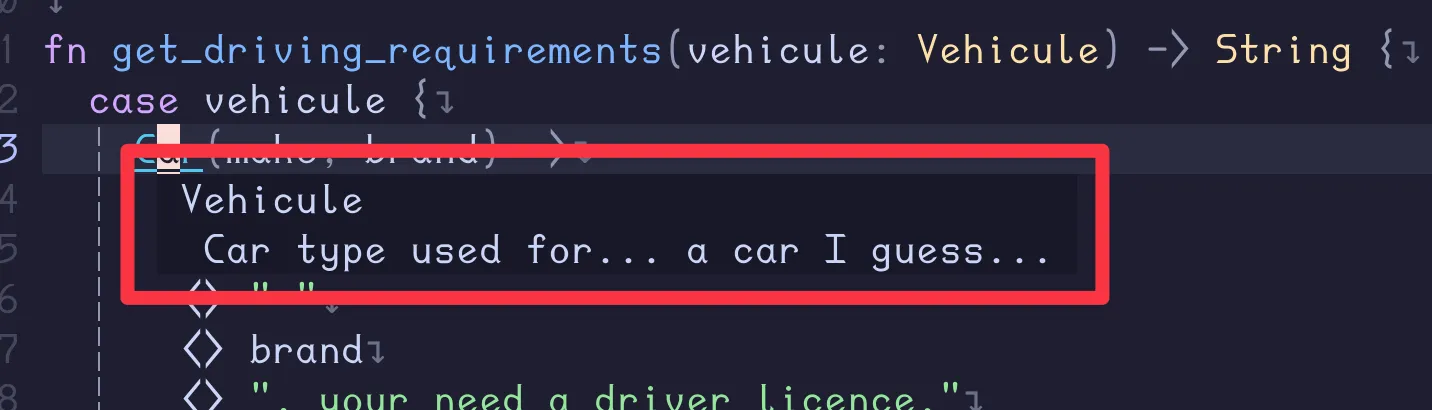
When I hover my mouse vehcule in my function body, I’m seeing:

LSP is capable of getting both type and documentation related to the variable.
Another exemple if, what happens when I hover on the Car constructor:
Here, the LSP shows both the parent custom type’name and the associated documentation.
One last example, when I hover on brand, for the code block executed when
Skateboard is matched:
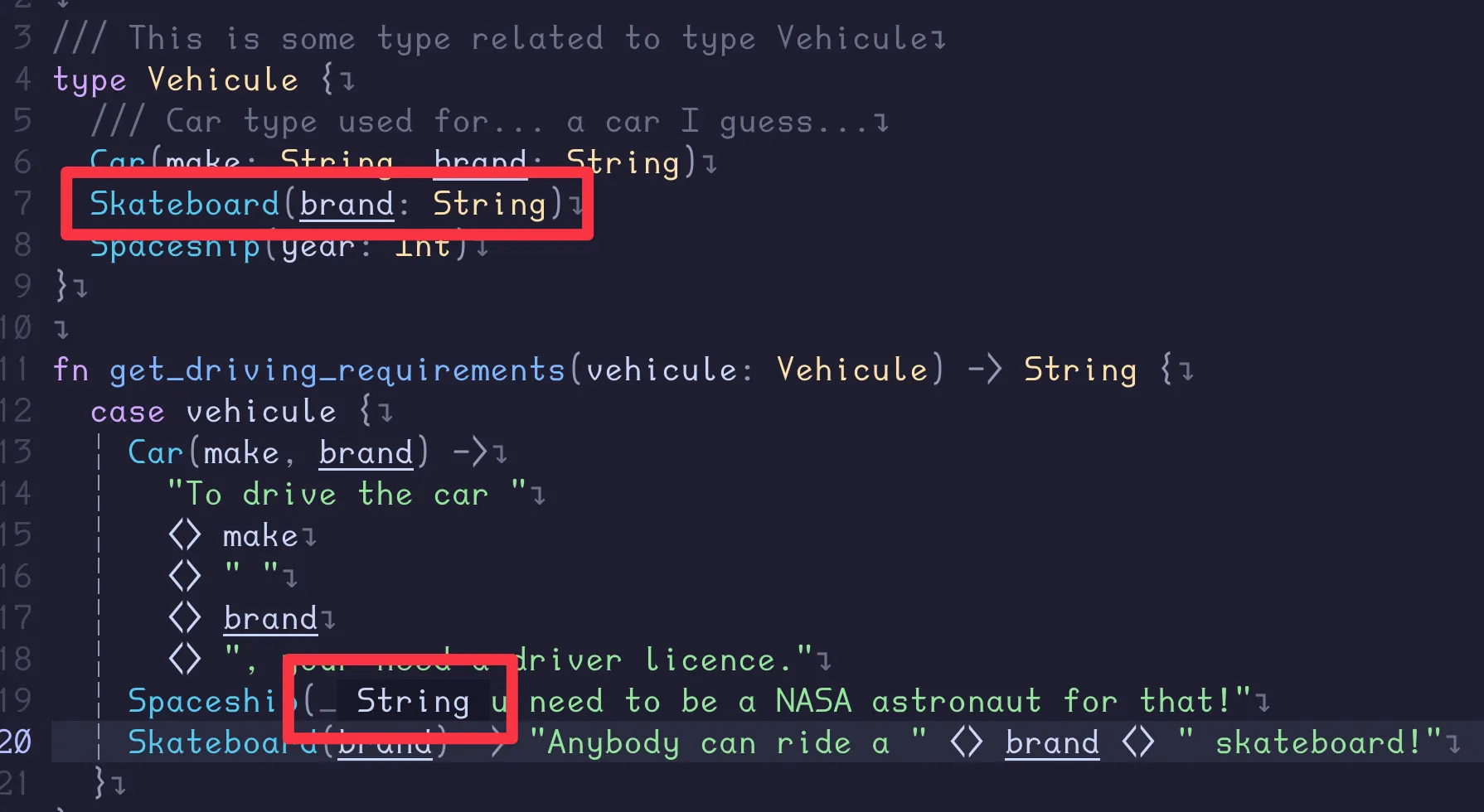
The LSP understands that brand is the first attribute in Skateboard.
This is the attention to details that makes you love an ecosystem. It helps you ship quality code, and it drives the language adoption up: this is a true win-win situation.
OTP implementation
Earlier, I told you that Gleam runs on the BEAM (never said that tbh). BEAM means Erlang, and Erlang means OTP. Please, sit down and relax, cuz I’m about to try to tell you what OTP is about.
OTP (Open Telecom Platform) is an architecture (and some kind of philosophy) for building fault-tolerant and highly concurrent software. The key principle is to divide a program into small execution units called processes (unrelated to OS processes) and making those processes communicate through message passing. Those processes can die at any time for any reason, so OTP advise you to put them under a supervision tree, so that a supervisor (which is also a process) can restart them. Erlang and Elixir give the developer the abstractions needed to build on top of OTP, with the BEAM allowing you to run MILLIONS of processes, even on a tiny server.
Dang, I really gave my everything on this one, but now you kind of know what OTP
is. That being said, Gleam also has its own OTP primitives, using an
external official package. The abstraction
I used the most is the actor (btw, you should learn about the actor model;
this thing is CRAZY). Let me show you how this works:
import gleam/io
import gleam/int
import gleam/erlang/process.{type Subject}
import gleam/otp/actor
type AsyncTaskMessage {
Increment(reply_to: Subject(Int))
Decrement(reply_to: Subject(Int))
}
fn handle_async_task(message: AsyncTaskMessage, state: Int) {
case message {
Increment(client) -> {
let new_value = state + 1
process.send(client, new_value)
actor.continue(new_value)
}
Decrement(client) -> {
let new_value = state - 1
process.send(client, new_value)
actor.continue(new_value)
}
}
}
fn start_async_task(state: Int) {
actor.start(state, handle_async_task)
}
fn main() {
let assert Ok(actor) = start_async_task(0)
let response = actor.call(actor, fn(subject) { Increment(subject) }, 10_000)
io.println("New value: " <> int.to_string(response))
}
For a Gleam actor, you need a few things:
- A custom type for all kind of messages your actor can receive. It’s called
AsyncTaskMessagein this example. - A function which takes a message and a state (the state being whatever you’d
like) and returns a new state, or something indicating that the task should
end. This is
handle_async_taskin our example. - A function starting everything. In our example this is the
start_asyncfunction.
With all of these pieces, you get a new stateful process that can live on its own. You can send messages for it to do… stuffs, I guess. Yeah, I know the demo is kind of lame, BUT it shows you how powerful Gleam’s type system is when coupled with OTP. You cannot send any message to your process that isn’t type-checked AT COMPILE TIME!
Something less cool, is the fact that OTP isn’t fully ported to Gleam. Few features, like Registries are missing…
Lustre, a curious web framework
YEAH, I KNOW, another new web framework. You have to understand, a new language needs that kind of popular tooling. Some people (web devs) are waiting for it. Lustre is a Gleam web framework. It’s been around in Gleam ecosystem for a long time and I think, is mature in Gleam’s context.
I didn’t tried it yet, (it should be one of my next article), but we’re talking about a tech with a lot of cool features:
- It’s isomorphic, it’s running on both backend and frontend.
- It’s heavily inspired from Elm, this scary thing we got from weed smoking Haskell geniuses (this is a compliment, huge respect for them).
- It’s opinionated, from an app to another, you supposed to see the same conventions and code structure.
I’ll let you check the documentation and see if it’s something that you’d be interrested in.
Javascript, interoperability
I JUST TOLD YOU!!! Gleam has a web framework and it’s ISOMORPHIC. How does it run on web? It runs because Gleam can transpile to Javascript. This is an interesting strategy. They are trying to convince the easiest crowd: Javascript developers. Those people (me, I’m “these people”) are tired of Typescript / Javascript nonsense. They’re looking for simplicity, robustness and Gleam has all the tool they need for that. There’s few players in this space, like ReasonML and ReScript.
Check the code below:
import gleam/io
type Vehicle {
Car(make: String, brand: String)
Skateboard(brand: String)
Spaceship(year: Int)
}
fn get_driving_requirements(vehicle: Vehicle) -> String {
case vehicle {
Car(make, brand) ->
"To drive the car "
<> make
<> " "
<> brand
<> ", your need a driver licence."
Spaceship(_) -> "You need to be a NASA astronaut for that!"
Skateboard(brand) -> "Anybody can ride a " <> brand <> " skateboard!"
}
}
pub fn main() {
Car(make: "Hyundai", brand: "Kona")
|> get_driving_requirements()
|> io.println()
}
This snippet is quite at exposing Gleam’s key features, there’s types, pattern
matching, pipe operator… See below the Javascript output after running
gleam build --target javascript:
import * as $io from "../gleam_stdlib/gleam/io.mjs";
import { CustomType as $CustomType } from "./gleam.mjs";
class Car extends $CustomType {
constructor(make, brand) {
super();
this.make = make;
this.brand = brand;
}
}
class Skateboard extends $CustomType {
constructor(brand) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
}
}
class Spaceship extends $CustomType {
constructor(year) {
super();
this.year = year;
}
}
function get_driving_requirements(vehicle) {
if (vehicle instanceof Car) {
let make = vehicle.make;
let brand = vehicle.brand;
return (
"To drive the car " + make + " " + brand + ", your need a driver licence."
);
} else if (vehicle instanceof Spaceship) {
return "You need to be a NASA astronaut for that!";
} else {
let brand = vehicle.brand;
return "Anybody can ride a " + brand + " skateboard!";
}
}
export function main() {
let _pipe = new Car("Hyundai", "Kona");
let _pipe$1 = get_driving_requirements(_pipe);
return $io.println(_pipe$1);
}
The JS code you’re getting is super understandable. You can read it, debug it and understand how Gleam transforms Gleam code into Javascript code. There are two important imports:
$io, which is library that matches what we have in the std libgleam/io.CustomType, which is a class imported fromprelude.mjs, that contains stuff Gleam needs when operating in a Javascript context.
What’s next with Gleam
We spoke briefly about everything interesting with Gleam. As you may have noticed, there’s nothing that I dislike, for now. I’ll keep experimenting while doing CodeCrafters puzzles (sponsored link). I’m currently building my own Redis with Gleam. Hit me up on Twitter or Twitch if you want to talk about it.